Editing The Book
Contents
Editing The Book#
Hi, welcome this is a short guide on getting set up with the project if you would like to contribute. This is a brief guide, and you will need to read the documentation provided.
Unfortunately, the Jupyter Book project is in the early stages and only has provisional support for windows. However, Windows users can use Windows subsystem for Linux(WSL). This should avoid any windows related compatibility problems. You can find instructions to set up WSL here.
We have not tested Jupyter Book on Mac Os, so your mileage may vary. There is always the option of running a linux virtual machine.
If you are new to Linux, The Ubuntu distro is very popular.
With some form of Linux install you will need a python and pip. First, check the system is up-to-date. All these commands are run in the BASH,
sudo apt update
Then install pip,
sudo apt install python3-pip
You can check that this has installed correctly with:
pip --version
Sometimes, you may need to use pip3 rather than pip in these commands, depending on how python is installed on your machine.
Setting Up a New Jupyter Book#
If you want to make a new project, then setting up one’s own book is quite simple. First download the package:
pip install -U jupyter-book
Now, I would recommend creating a virtual environment, this enables you to have a siloed version of python to work from so that it does not affect your other work. Creating a folder to contain the project is sensible. Navigate in the shell to this folder:
cd /path/to/my/project/folder/
for example:
mkdir ~/Documents/ClimateBook
cd ~/Documents/ClimateBook
from here create a virtual environment:
pip install -U venv
pip install -U virtualenv
Here you replace the_name_of_the_environment, with a name for your environment.
python3 -m venv the_name_of_the_environment
Now activate that environment from the directory in which you created the environment:
source ./the_name_of_the_environment/bin/activate
We now create the book:
jupyter-book create mynewbook/
This will create a new jupyter book with a _toc.yml and a .config.yml.
This template book can be edited. Full details on how to use the books are provided on the Jupyter Book
Toc and Config#
Adding content to the book and customising the book is managed by the _toc.yml and _config.yml files.
An example of the config file is shown below:
# In _config.yml
title: My sample book
author: The Jupyter Book Community
logo: logo.png
execute:
execute_notebooks: force
# Add a bibtex file so that we can create citations
bibtex_bibfiles:
- references.bib
Any file references, such as references or a logo, must have their path defined if they are not in the same directory. This file controls further customisation of the book’s compilation and is described here.
The _toc.yml table of contents file controls how content is added to the book. Jupyter Book, compared to other markdown book formats, incorporates Jupyter notebook files and markdown content. Adding files can now be done by adding their path to the chapters list. There are alternative structuring methods other than chapters within the Framework.
# In _toc.yml
format: jb-book
root: intro
chapters:
- file: path/to/markdown.md
- file: path/to/notebook.ipynb
The root file defines the landing page and refers to a markdown file.
Editing This Book#
Rather than making your own Jupyter Book it can be copied and edited. The instructions below walk through creating a local git copy of the CDS_book repo. First installing and setting up git:
sudo apt install git
Connect to your GitHub with:
git config --global user.name "your github username"
git config --global user.email "your github emial"
Now navigate to the folder in which you want to store the project. From there perform a git clone:
git clone https://github.com/seancraven/CDS_book.git
In the cloned files, there is a requirements.txt file, from which all the required packages can be installed, first we install the virtual environments package:
pip install -U virtualenv
Here you replace the_name_of_the_environment, with a name for your environment.
python3 -m venv the_name_of_the_environment
Now activate that environment from the directory in which you created the environment:
source ./the_name_of_the_environment/bin/activate
With the environment activated all the required packages can be installed,
pip install -r requirements.txt
With the environment for the book set up it can be built.
Note
You may also have to install some packages into your base python environment because of how jb books work.
The build command is targeted at a directory with the _config.yml and _toc.yml. If you have cloned the git repositor, these will be in the CDS_book directory. From here
jupyter-book build /path/to/book/
This will provide you with a HTML document that can be opened in a web browser.
Publishing a Jupyter Book#
Jupyter Book is integrated with GitHub pages, this makes it easy to publish updates to your book in one line from the terminal. The GitHub pages package can be obtained with a normal pip install:
pip install ghp-import
Before the project can be published on a GitHub page it needs a GitHub repo. The first author of the book doesn’t maintain the repository it is better that new iterations clone and publish new cloned repos. This means a new project repo should be made on GitHub. When you make this repo do not initialise it with any files such as a readme or a licence.
Once you have logged into Github to make a new repo click the + button in the top right hand corner:
 From here set up an empty repository:
From here set up an empty repository:
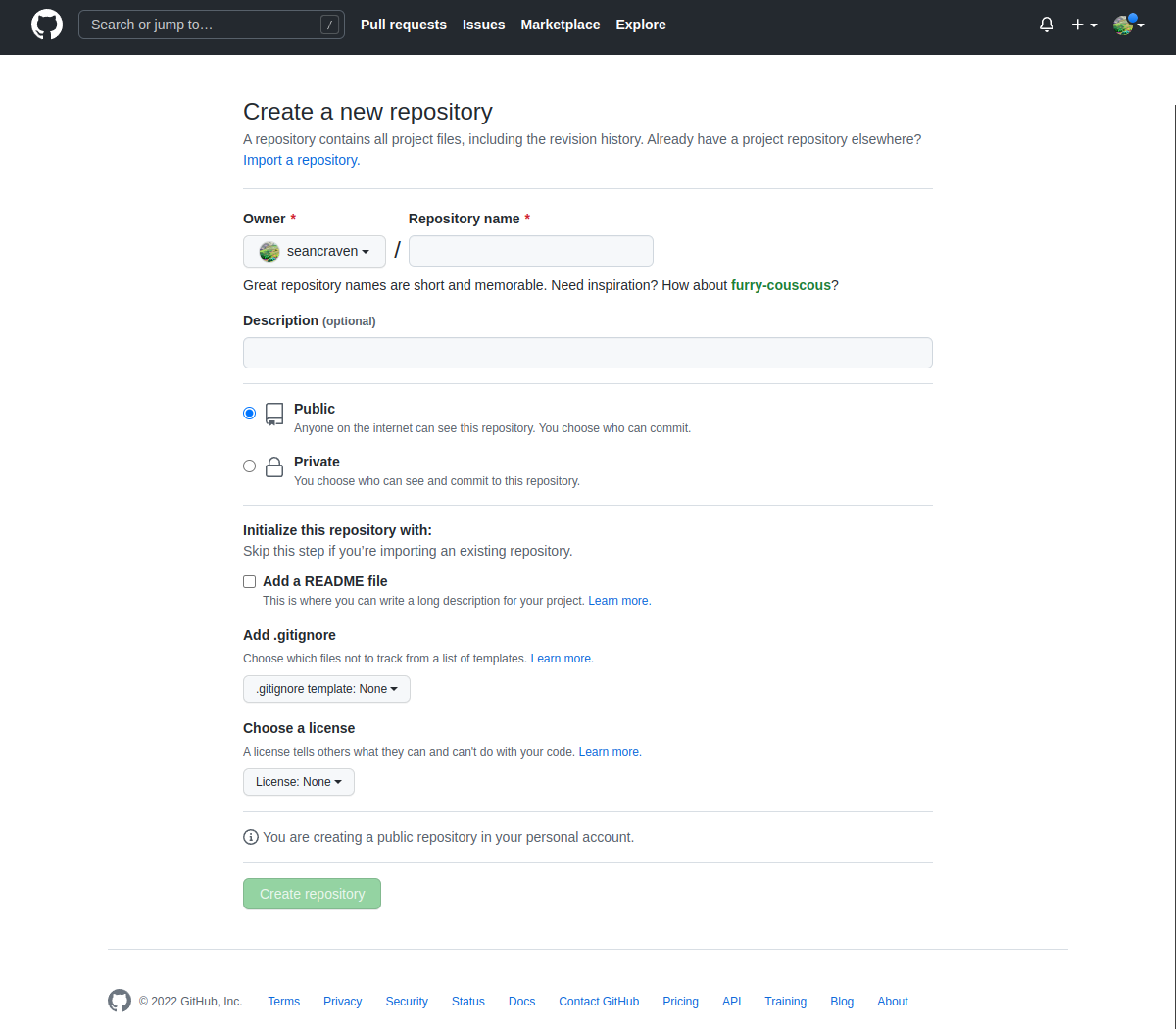 Now you can follow the following prompts depending on what you are looking to do, clone or set up a new repo.
Now you can follow the following prompts depending on what you are looking to do, clone or set up a new repo.
Tip
When working with GitHub if you are asked for a password in the shell, this is not the website password but a pat key that you can generate from your github page online. Instructions are found here
If you cloned the previous environment, then you will have to rename the original remote, otherwise skip this command:
git remote rename origin upstream
Add your GitHub remote repo:
git remote add origin https://github.com/your-account/your-repository.git
Finally, we push the content to the repo:
git push origin main
Note
If you are setting a book up from scratch you will need to add some files to the main GitHub repository, before pushing. This is done by performing
git add filname
then commit your changes:
git commit -m "first commit"
After this your can proceed with a push
Now with the version control setup, you can record changes with commits and store all the work on GitHub. Git can be hard to learn, and making mistakes can be even harder to fix. Stackexchange is your friend as well as ohshitgit.
The GitHub page can be set up easily with a repo for the project. First, navigate to the main directory where the _build folder of the book is located and run
ghp-import -n -p -f _build/html
The website can then be found through the pages section of your repository.
